本文共 13934 字,大约阅读时间需要 46 分钟。
Python 和 C 的混合编程工具有很多,这里介绍 Python 标准库自带的 ctypes 模块的使用方法。
- 初识
Python 的 ctypes 要使用 C 函数,需要先将 C 编译成动态链接库的形式,即 下的 .dll 文件,或者 Linux 下的 .so 文件。先来看一下 ctypes 怎么使用 C 标准库。
Windows 系统下的 C 标准库动态链接文件为 msvcrt.dll (一般在目录 C:\Windows\System32 和 C:\Windows\SysWOW64 下分别对应 32-bit 和 64-bit,使用时不用刻意区分,Python 会选择合适的)
Linux 系统下的 C 标准库动态链接文件为 libc.so.6 (以 64-bit Ubuntu 系统为例, 在目录 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu 下)
例如,以下代码片段导入 C 标准库,并使用 printf 函数打印一条消息,
import platformfrom ctypes import *
if platform.system() == ‘Windows’:
libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(‘msvcrt.dll’) elif platform.system() ==‘Linux’: libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(‘libc.so.6’)libc.printf(‘Hello ctypes!\n’)
另外导入dll文件,还有其它方式如下,详细解释请参阅 ctypes module 相关文档,
import platform from ctypes import *
if platform.system() == ‘Windows’:
libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(‘msvcrt.dll’) #libc = windll.LoadLibrary(‘msvcrt.dll’) # Windows only #libc = oledll.LoadLibrary(‘msvcrt.dll’) # Windows only #libc = pydll.LoadLibrary(‘msvcrt.dll’)#libc = CDLL('msvcrt.dll')#libc = WinDLL('msvcrt.dll') # Windows only#libc = OleDLL('msvcrt.dll') # Windows only#libc = PyDLL('msvcrt.dll')
elif platform.system() ==‘Linux’:
libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(‘libc.so.6’) #libc = pydll.LoadLibrary(‘libc.so.6’)#libc = CDLL('libc.so.6')#libc = PyDLL('libc.so.6')libc.printf('Hello ctypes!\n')
- ctypes 数据类型
ctypes 作为 Python 和 C 联系的桥梁,它定义了专有的数据类型来衔接这两种编程语言。如下表,
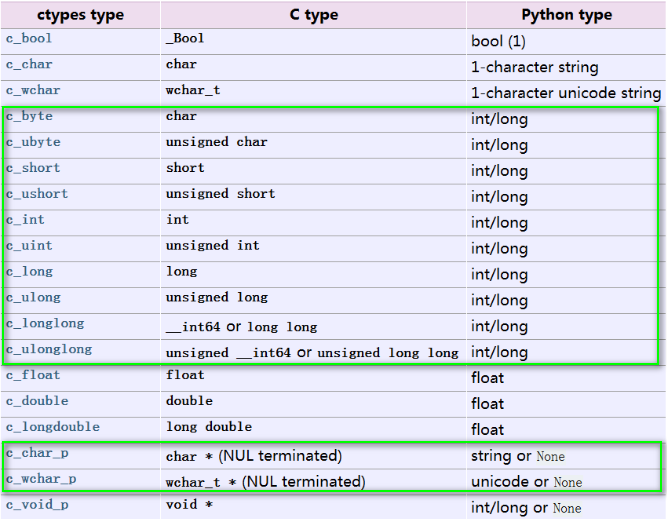
注:Python 中的类型,除了 None,int, long, Byte String,Unicode String 作为 C 函数的参数默认提供转换外,其它类型都必须显式提供转换。
None:对应 C 中的 NULL
int, long: 对应 C 中的 int,具体实现时会根据机器字长自动适配。
Byte String:对应 C 中的一个字符串指针 char * ,指向一块内存区域。
Unicode String :对应 C 中一个宽字符串指针 wchar_t *,指向一块内存区域。
例如,
import platformfrom ctypes import *
if platform.system() == ‘Windows’:
libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(‘msvcrt.dll’) elif platform.system() == ‘Linux’: libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(‘libc.so.6’)libc.printf(’%s\n’, ‘here!’) # here!
libc.printf(’%S\n’, u’there!’) # there! libc.printf(’%d\n’, 42) # 42 libc.printf(’%ld\n’, 60000000) # 60000000#libc.printf(’%f\n’, 3.14) #>>> ctypes.ArgumentError
#libc.printf(’%f\n’, c_float(3.14)) #>>> dont know why 0.000000 libc.printf(’%f\n’, c_double(3.14)) # 3.140000
- 创建可变的 string buffer
Python 默认的 string 是不可变的,所以不能传递 string 到一个 C 函数去改变它的内容,所以需要使用 create_string_buffer,对应 Unicode 字符串,要使用 create_unicode_buffer,
定义和用法如下,
>>> help(create_string_buffer) Help on function create_string_buffer in module ctypes:
create_string_buffer(init, size=None)
create_string_buffer(aString) -> character array create_string_buffer(anInteger) -> character array create_string_buffer(aString, anInteger) -> character arrayfrom ctypes import *
p = create_string_buffer(5)
print sizeof§ # 5 print repr(p.raw) # ‘\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00’ p.raw = ‘Hi’ print repr(p.raw) # ‘Hi\x00\x00\x00’ print repr(p.value) # ‘Hi’
- 传递自定义参数类型到 C 函数
ctypes 允许你创建自定义参数类型,它会自动去搜索自定义数据的 _as_parameter 属性,将其作为 C 函数的参数,例如,
import platform from ctypes import *
if platform.system() == ‘Windows’:
libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(‘msvcrt.dll’) elif platform.system() == ‘Linux’: libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(‘libc.so.6’)class Bottles(object):
def init(self, number): self.as_parameter = number # here only accept integer, string, unicode string bottles = Bottles(42) libc.printf(’%d bottles of beer\n’, bottles)输出,
42 bottles of beer
也可以为你的数据定义 _as_parameter 属性,如下,
import platform from ctypes import *
if platform.system() == ‘Windows’:
libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(‘msvcrt.dll’) elif platform.system() == ‘Linux’: libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(‘libc.so.6’)class Bottles(object):
def init(self): self.as_parameter = None # only accept integer, string, unicode string @property def aspram(self): return self.as_parameter@aspram.setterdef aspram(self, number): self._as_parameter_ = number
bottles = Bottles()
bottles.aspram = 63 libc.printf(’%d bottles of beer\n’, bottles)输出,
63 bottles of beer
- 指定 C 函数的参数类型
可以指定要调用 C 函数的参数类型,如果传入参数不符合指定的类型,则 ctypes 会尝试转换,如果转换不成功,则抛 ArgumentError,例如,
import platform from ctypes import *
if platform.system() == ‘Windows’:
libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(‘msvcrt.dll’) elif platform.system() == ‘Linux’: libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(‘libc.so.6’)libc.printf.argtypes = [c_char_p, c_char_p, c_int, c_double]
libc.printf(‘String is “%s”, Int is %d, Double is %f\n’, ‘Hi’, 10, 2.2)
libc.printf(’%s, %d, %f\n’, ‘X’, 2, 3) try: libc.printf("%d %d %d", 1, 2, 3) except ArgumentError, e: print “*** ERROR: %s” % str(e)输出,
String is “Hi”, Int is 10, Double is 2.200000 X, 2, 3.000000 *** ERROR: argument 2:: wrong type
- 指定 C 函数的返回值类型
如果不指定 C 函数的返回值, ctypes 默认返回 int 类型,如果要返回特定类型,需要指定返回类型 restype,
例如,
import platform from ctypes import *
if platform.system() == ‘Windows’:
libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(‘msvcrt.dll’) elif platform.system() == ‘Linux’: libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(‘libc.so.6’)print ‘1->’, libc.strchr(‘abcdefghij’, c_char(‘d’))
libc.strchr.restype = c_char_p
print ‘2->’, libc.strchr(‘abcdefghij’, c_char(‘d’))
print ‘3->’, libc.strchr(‘abcdefghij’, ‘d’) # Note, here C function strchr not know what ‘d’ mean, so rerurn None libc.strchr.argtypes = [c_char_p, c_char] print ‘4->’, libc.strchr(‘abcdefghij’, ‘d’) # Note, here not use c_char(‘w’)输出:
1-> 40291315 2-> defghij 3-> None 4-> defghij
- 按引用传递参数
有些情况下,需要 C 函数修改传入的参数,或者参数过大不适合传值,需要按引用传递,ctypes 提供关键字 byref() 处理这种情况,
例如,
import platform from ctypes import *
if platform.system() == ‘Windows’:
libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(‘msvcrt.dll’) elif platform.system() == ‘Linux’: libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(‘libc.so.6’)i = c_int()
f = c_float() s = create_string_buffer(’\000’ * 32) print ‘i.val =’, i.value print ‘f.val =’, f.value print ‘repr(s.value) =’, repr(s.value) libc.sscanf(‘1 3.14 Hello’, ‘%d %f %s’, byref(i), byref(f), s) print ‘after, i.val =’, i.value print ‘after, f.val =’, f.value print ‘after, repr(s.value) =’, repr(s.value)输出,
i.val = 0 f.val = 0.0 repr(s.value) = ‘’ after, i.val = 1 after, f.val = 3.1400001049 after, repr(s.value) = ‘Hello’
- 使用结构体
ctypes 支持结构体的使用,从 Structure 类派生,数据放在 fields 中,
例如,
class Point(Structure): fields = [(‘x’, c_int), (‘y’, c_int)]
point = Point(10, 20)
print ‘point.x =’, point.x print ‘point.y =’, point.ypoint = Point(y=5)
print ‘after, point.x =’, point.x print ‘after, point.y =’, point.y printclass Rect(Structure):
fields = [(‘upperleft’, Point), (‘lowerright’, Point)]rc = Rect(point)
print ‘rc.upperleft.x = %d, rc.upperleft.y = %d’ % (rc.upperleft.x, rc.upperleft.y) print ‘rc.lowerright.x = %d, rc.lowerright.y = %d’ % (rc.lowerright.x, rc.lowerright.y)r = Rect(Point(1, 2), Point(3, 4))
print ‘r.upperleft.x = %d, r.upperleft.y = %d’ % (r.upperleft.x, r.upperleft.y) print ‘r.lowerright.x = %d, r.lowerright.y = %d’ % (r.lowerright.x, r.lowerright.y)输出,
point.x = 10 point.y = 20 after, point.x = 0 after, point.y = 5
rc.upperleft.x = 0, rc.upperleft.y = 5
rc.lowerright.x = 0, rc.lowerright.y = 0 r.upperleft.x = 1, r.upperleft.y = 2 r.lowerright.x = 3, r.lowerright.y = 4
- 位域
ctypes 提供了对位域的支持,
例如,
class IntBit(Structure): fields = [(‘x’, c_uint, 2), (‘y’, c_uint, 4)]
IB = IntBit(1, 15)
print ‘IB.x = %d’ % IB.x print ‘IB.y = %d’ % IB.yIB2 = IntBit(4, 16)
print ‘-> IB2.x = %d’ % IB2.x print ‘-> IB2.y = %d’ % IB2.y输出,
IB.x = 1 IB.y = 15 -> IB2.x = 0 -> IB2.y = 0
- 数组
ctypes 提供了对 Array 的支持,
例如,
TenIntArrayType = c_int * 10 ta = TenIntArrayType(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10) for item in ta: print item, print
class PointEx(Structure):
fields = [(‘x’, c_int), (‘y’, c_int)]class MyStruct(Structure):
fields = [(‘a’, c_int), (‘b’, c_int), (‘pointex_array’, PointEx * 4)]ms = MyStruct(4, 5, ((1,1), (2,2), (3,3), (4,4)))
for item in ms.pointex_array: print ‘(item.x, item.y) = (%d, %d)’ % (item.x, item.y) print输出,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 (item.x, item.y) = (1, 1) (item.x, item.y) = (2, 2) (item.x, item.y) = (3, 3) (item.x, item.y) = (4, 4)
- 指针
ctypes 使用关键字 pointer 提供了对指针的支持,注意指针解引用使用 [0],
例如,
i = c_int(42) print ‘before, i.value =’, i.value pi = pointer(i) pi[0] = 57 print ‘after, i.value =’, i.value
# create NULL pointer, also can use this way, but recommend use ‘pointer’ not ‘POINTER’
null_ptr = POINTER(c_int)() print ‘bool(null_ptr) =’, bool(null_ptr)输出,
before, i.value = 42 after, i.value = 57 bool(null_ptr) = False
- 类型转换
ctypes 提供了类型转换方法 cast(),
例如,
class Bar(Structure): fields = [(‘count’, c_int), (‘value’, POINTER(c_int))]
bar = Bar()
bar.count = 3 bar.value = (c_int * 3)(1, 2, 3) for idx in range(bar.count): print ‘bar.value[%d] = %d’ % (idx, bar.value[idx])## use cast to convert
try: bar.value = (c_byte * 4)() except TypeError, e: print ‘*** ERROR: %s’ % str(e)bar.value = cast((c_byte * 4)(), POINTER(c_int))
for idx in range(4): print ‘now, bar.value[%d] = %d’ % (idx, bar.value[idx]) print输出,
bar.value[0] = 1 bar.value[1] = 2 bar.value[2] = 3 *** ERROR: incompatible types, c_byte_Array_4 instance instead of LP_c_long instance now, bar.value[0] = 0 now, bar.value[1] = 0 now, bar.value[2] = 0 now, bar.value[3] = 0
- 回调函数
ctypes 通过 CFUNCTYPE 支持回调函数,
例如,
import platform from ctypes import *
if platform.system() == ‘Windows’:
libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(‘msvcrt.dll’) elif platform.system() == ‘Linux’: libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(‘libc.so.6’)IntArray5 = c_int * 5
ia = IntArray5(5, 1, 7, 33, 99)# CFUNCTYPE(restype, *argtypes, **kw)
CmpFuncType = CFUNCTYPE(c_int, POINTER(c_int), POINTER(c_int))def py_cmp_func(a, b):
if a[0] > b[0]: return 1 elif a[0] < b[0]: return -1 else: return 0cmpfunc = CmpFuncType(py_cmp_func)
print 'before sort, the ia list is: ',
for item in ia: print item,# void qsort (void* base, size_t num, size_t size, int (compar)(const void,const void*));
libc.qsort(ia, len(ia), sizeof(c_int), cmpfunc)print '\nafter sort, the ia list is: ',
for item in ia: print item, print输出,
before sort, the ia list is: 5 1 7 33 99 after sort, the ia list is: 1 5 7 33 99
- Resize Space
ctypes 提供了 resize 变量占用空间的方法 resize(),注意,只能增大,不能小于原始空间,
例如,
short_array = (c_short * 4)(1, 2, 3, 4) print ‘sizeof(short_array) =’, sizeof(short_array) # get 8, means short_array take 8-byte memory print ‘len(short_array) =’, len(short_array) print 'before resize, short_array is: ', for idx in range(len(short_array)): print short_array[idx], print
try:
resize(short_array, 4) # resize short_array to 4-byte, raise error, due to cannot resize smaller than original except ValueError, e: print ‘ERROR: %s’ % str(e)resize(short_array, 32)
print ‘after succeed resize to 32-byte, now sizeof(short_array) =’, sizeof(short_array) print ‘after succeed resize to 32-byte, now len(short_array) =’, len(short_array) print 'after reszie, short_array is: ', for idx in range(len(short_array)): print short_array[idx],输出,
sizeof(short_array) = 8 len(short_array) = 4 before resize, short_array is: 1 2 3 4 ERROR: minimum size is 8 after succeed resize to 32-byte, now sizeof(short_array) = 32 after succeed resize to 32-byte, now len(short_array) = 4 after reszie, short_array is: 1 2 3 4
- Other
class cell(Structure): pass cell.fields = [(‘name’, c_char_p), (‘next’, POINTER(cell))]
c1 = cell()
c2 = cell() = ‘foo’ = ‘bar’ c1.next = pointer(c2) c2.next = pointer(c1)p = c1
for i in range(10): print , p = p.next[0]输出,
foo bar foo bar foo bar foo bar foo bar
- 坑
ctypes 相对于其它工具,使用起来有点繁琐,而且有很多坑,需要,
例如,
class POINT(Structure): fields = [(‘x’, c_int), (‘y’, c_int)]
class RECT(Structure):
fields = [(‘a’, POINT), (‘b’, POINT)]p1 = POINT(1, 2)
p2 = POINT(3, 4) rc = RECT(p1, p2)print ‘rc.a.x =’, rc.a.x
print ‘rc.a.y =’, rc.a.y print ‘rc.b.x =’, rc.b.x print ‘rc.b.y =’, rc.b.yrc.a, rc.b = rc.b, rc.a
print ‘after swap, bad result due to this is the pointer,’
print ‘rc.a.x =’, rc.a.x print ‘rc.a.y =’, rc.a.y print ‘rc.b.x =’, rc.b.x print ‘rc.b.y =’, rc.b.y print输出,
rc.a.x = 1 rc.a.y = 2 rc.b.x = 3 rc.b.y = 4 after swap, bad result due to this is the pointer, rc.a.x = 3 rc.a.y = 4 rc.b.x = 3 rc.b.y = 4
- Load 自定义 DLL
以 C 函数文件 needforspeed.c 为例,
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------- // Purpose: this c module is used to speed up the Python program, should be // compiled into dll, and then load into Python module with ctypes // method. // // Compile Methods: // // ====================== // Windows: use MSVC, x64 // ====================== // // C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio 12.0\VC\bin\amd64> cl /LD needforspeed.c /o nfs.dll // // ====== // Linux: // ====== // // $ gcc -fPIC -shared needforspeed.c -o //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- #include
// Windows need this compile direction for dll compilation, Linux no need
#ifdef _MSC_VER #define DLL_EXPORT __declspec( dllexport ) #else #define DLL_EXPORT #endifDLL_EXPORT void hello_world(void) {
printf(“Hello world!\n”); }DLL_EXPORT int mod(int m, int n) {
return m % n; }DLL_EXPORT int get_array_elem(int arr[], int idx) {
return arr[idx]; }DLL_EXPORT int get_array2D_elem(int arr[][3], int row, int col) {
return arr[row][col]; }在 Windows 下编译为 nfs.dll, 在 Linux 下编译为 ,Python 中调用如下,
import platform from ctypes import *
if platform.system() == ‘Windows’:
mylib = cdll.LoadLibrary(’./nfs.dll’) elif platform.system() == ‘Linux’: mylib = cdll.LoadLibrary(’./nfs.so’)mylib.hello_world()
printmod_rtv = mylib.mod(c_int(10), c_int(4))
print ‘mod_rtv(10 % 4) =’, mod_rtv print#####################
# 1D array get elem # ##################### IntArray10Type = c_int * 10 intArray = IntArray10Type() for idx in range(10): intArray[idx] = idx**2for idx in range(10):
print ‘intArray[%d] = %d’ % (idx, mylib.get_array_elem(intArray, idx)) print#####################
# 2D array get elem # ##################### IntArray3Col = c_int * 3 IntArray3Row3Col = IntArray3Col * 3 arr2d = IntArray3Row3Col(IntArray3Col(1, 2, 3), IntArray3Col(8, 9, 4), IntArray3Col(7, 6, 5))print ‘arr2d is:’
for r in range(3): for c in range(3): print '%d ’ % mylib.get_array2D_elem(arr2d, r, c), print输出,
Hello world!
mod_rtv(10 % 4) = 2
intArray[0] = 0
intArray[1] = 1 intArray[2] = 4 intArray[3] = 9 intArray[4] = 16 intArray[5] = 25 intArray[6] = 36 intArray[7] = 49 intArray[8] = 64 intArray[9] = 81arr2d is:
1 2 3 8 9 4 7 6 5
完。
转载地址:http://vqesn.baihongyu.com/